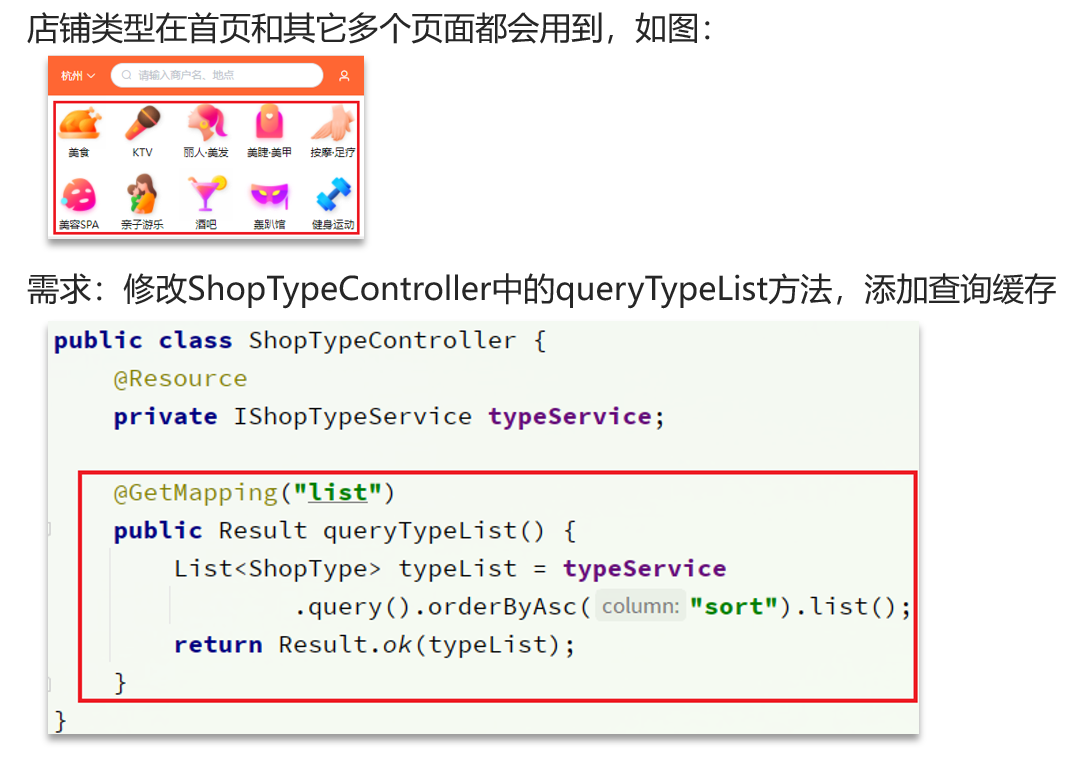
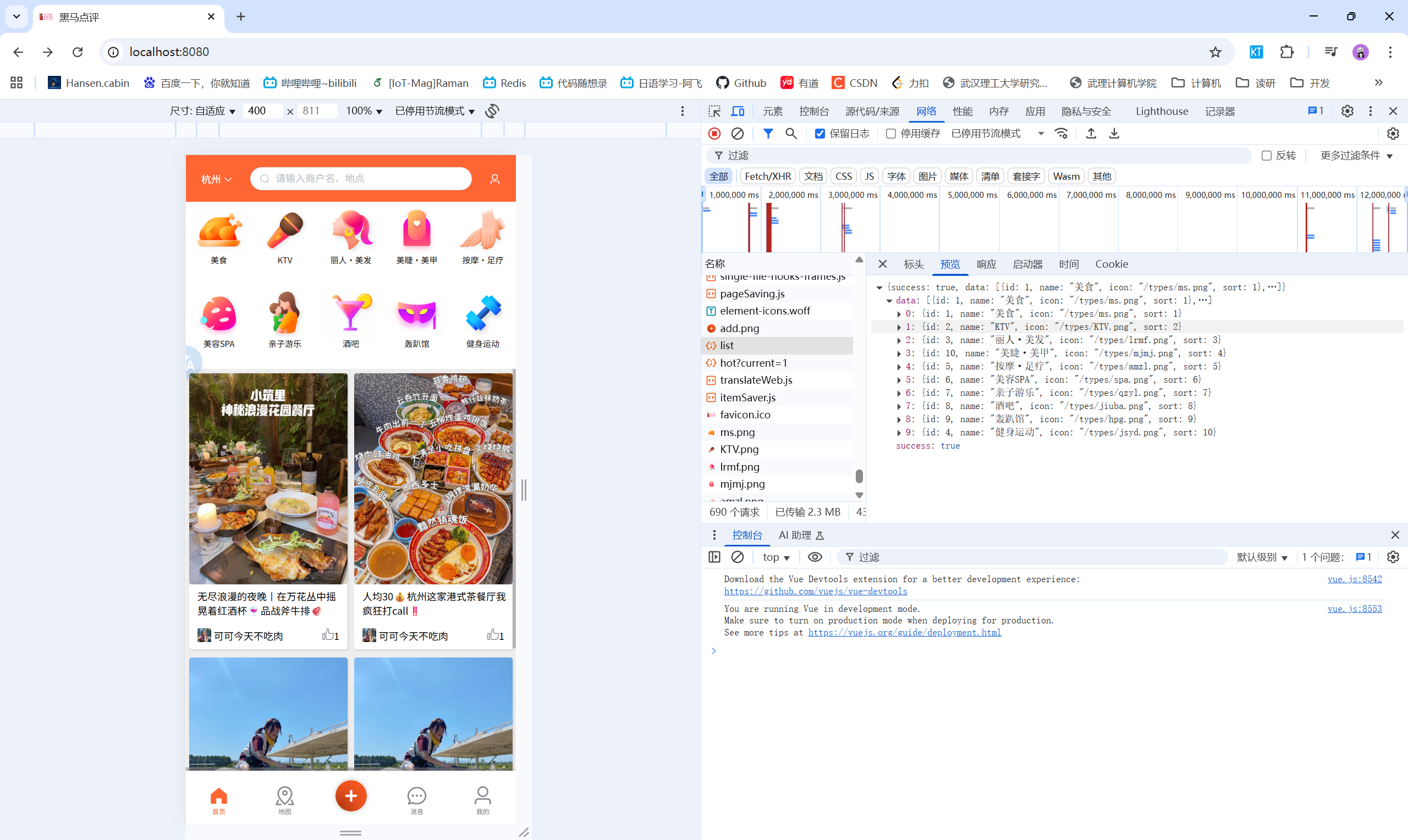
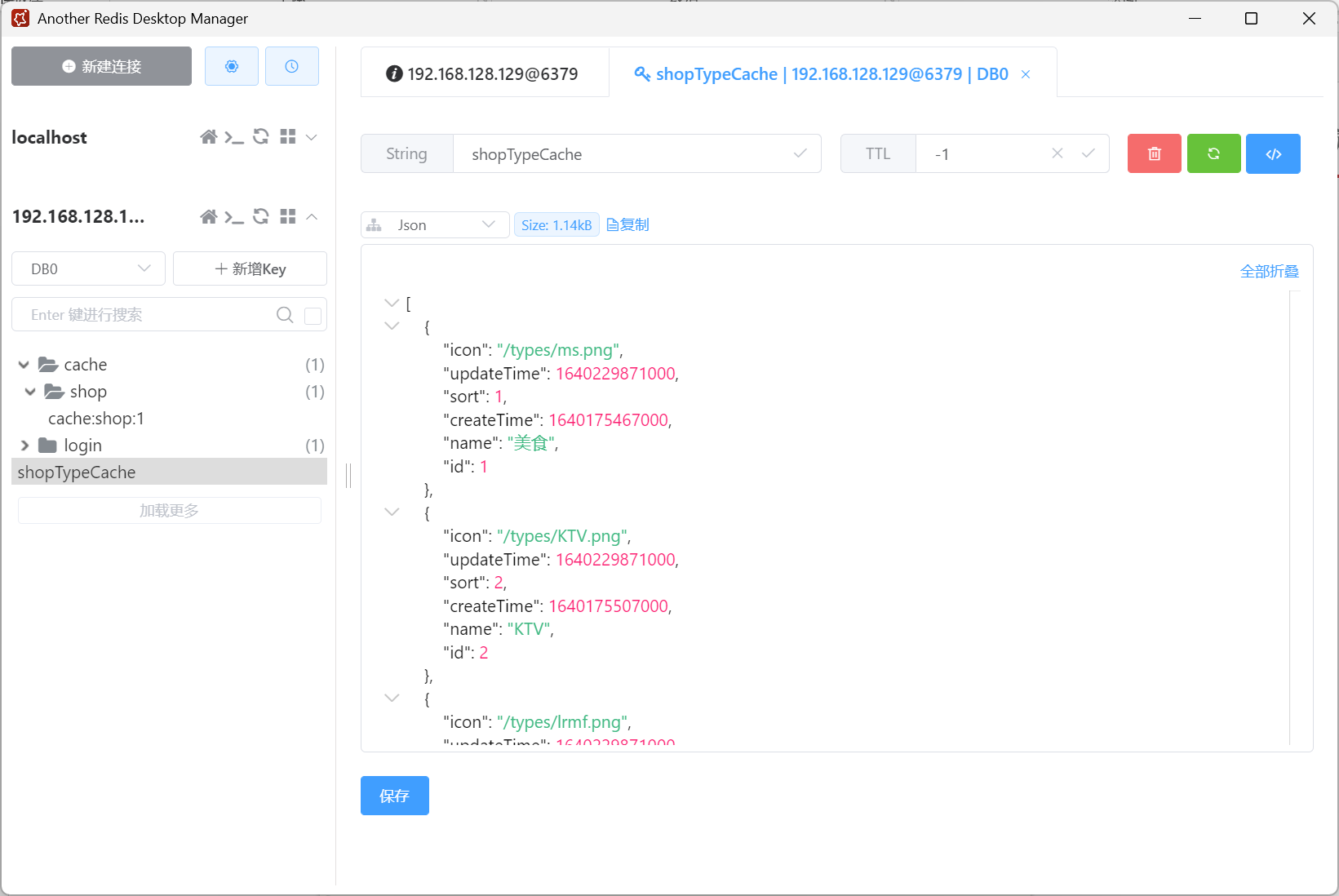
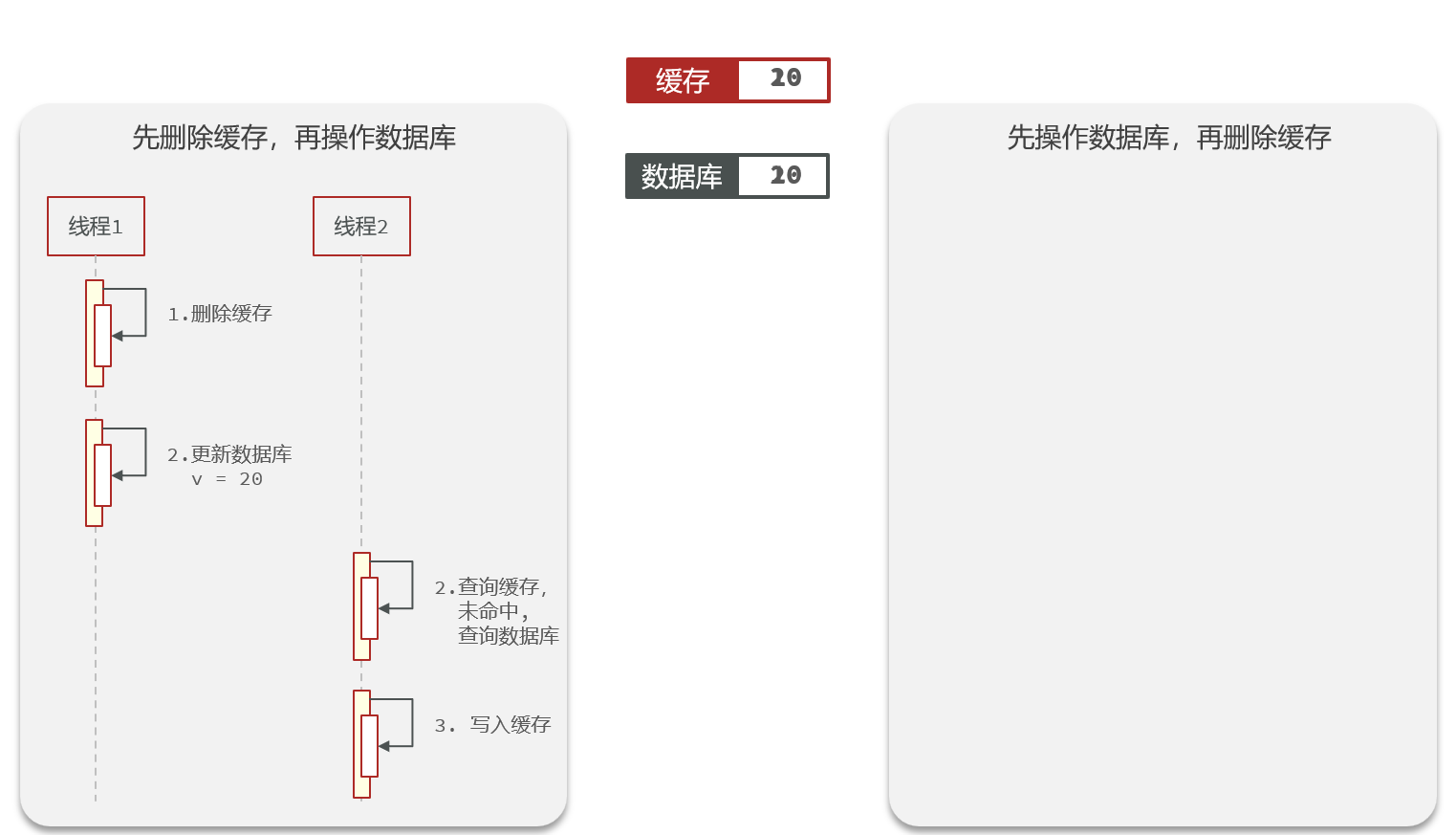
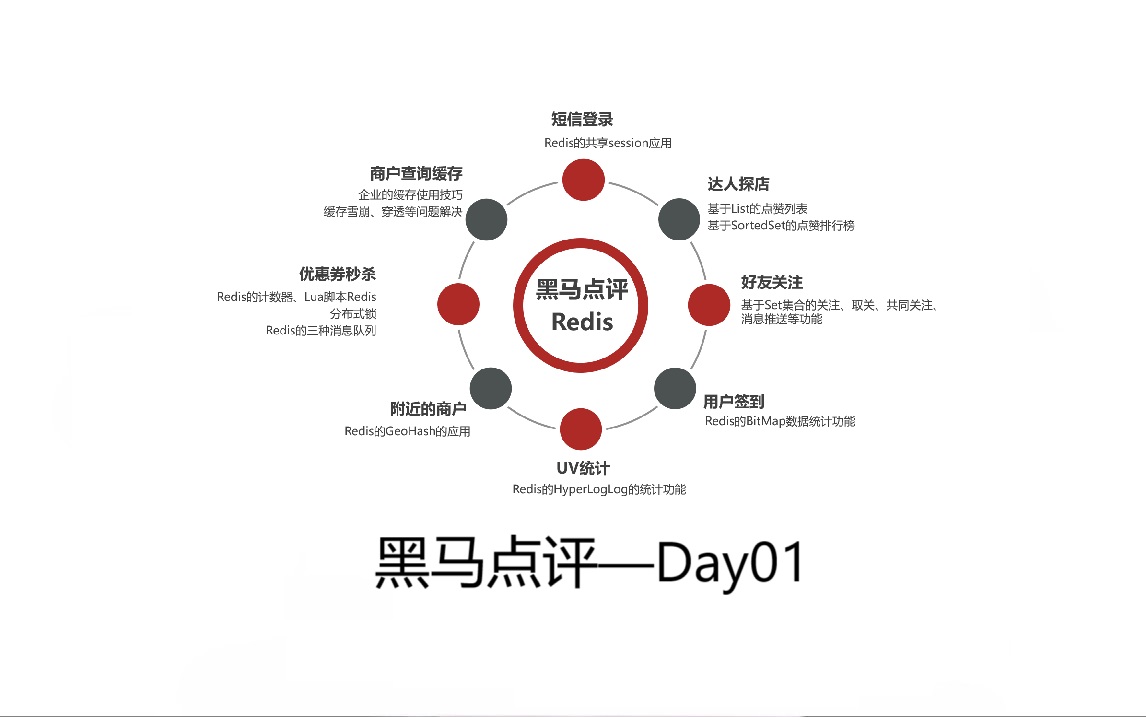
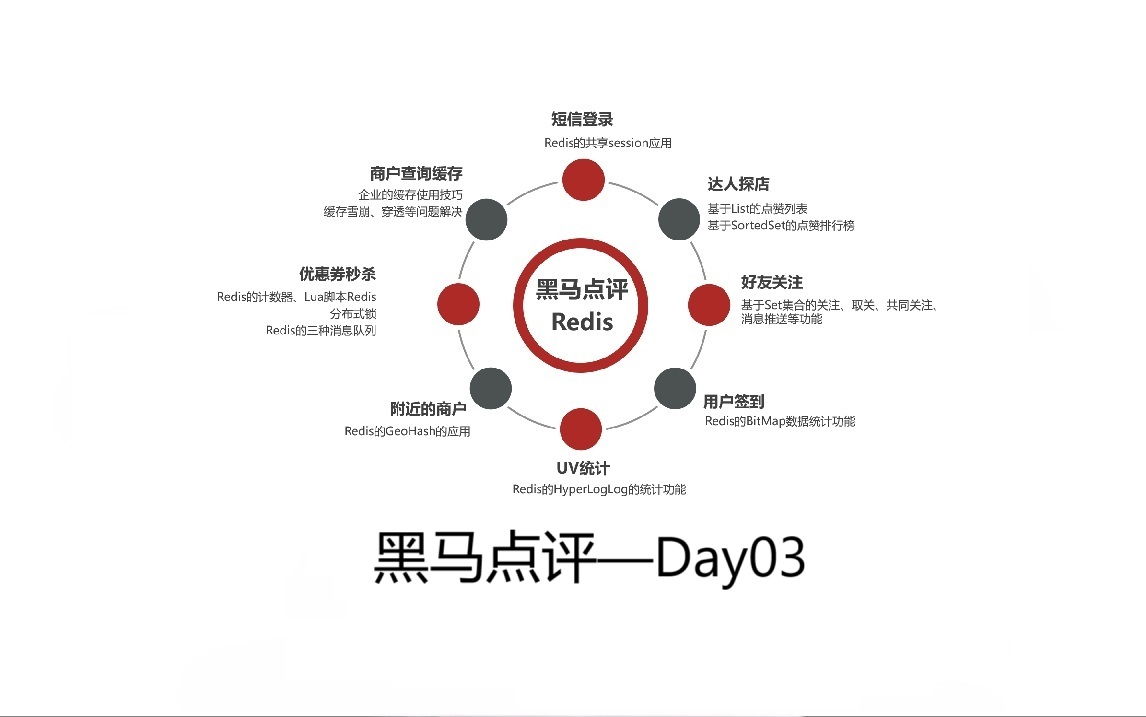
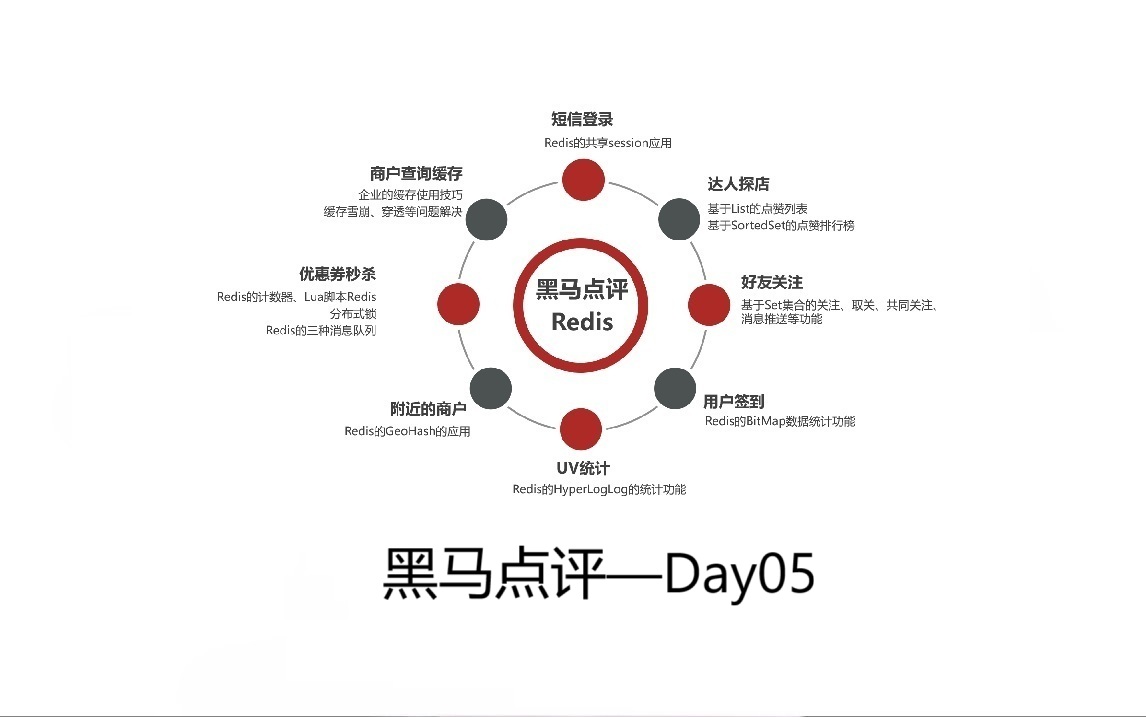
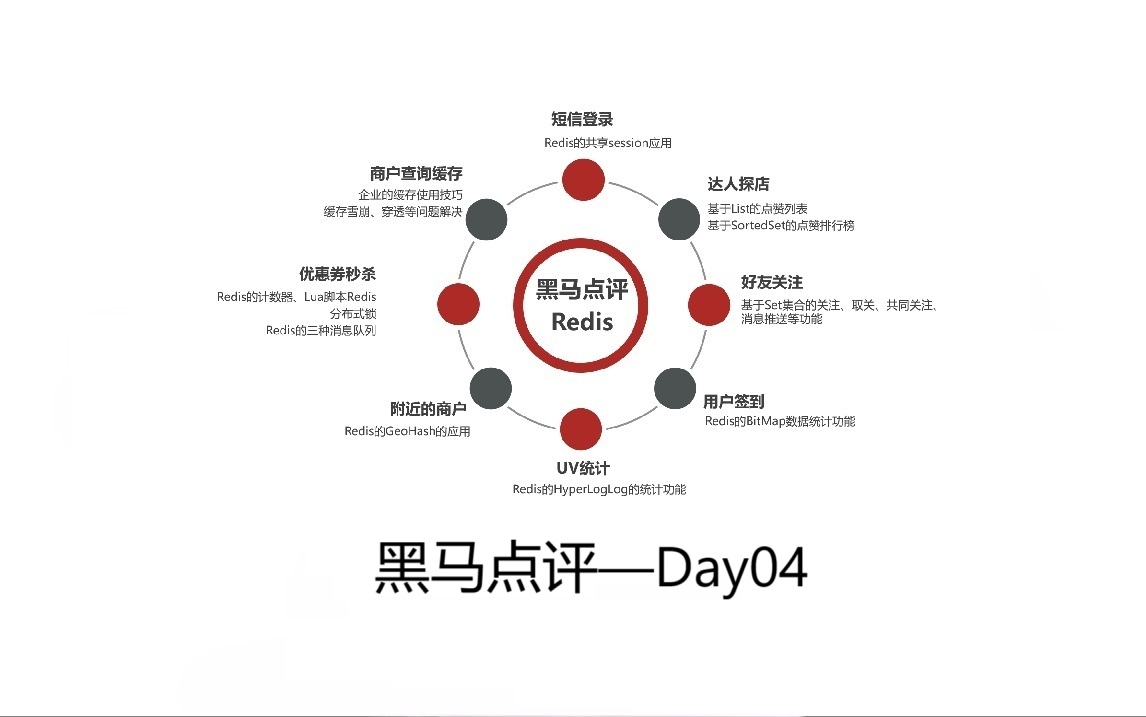
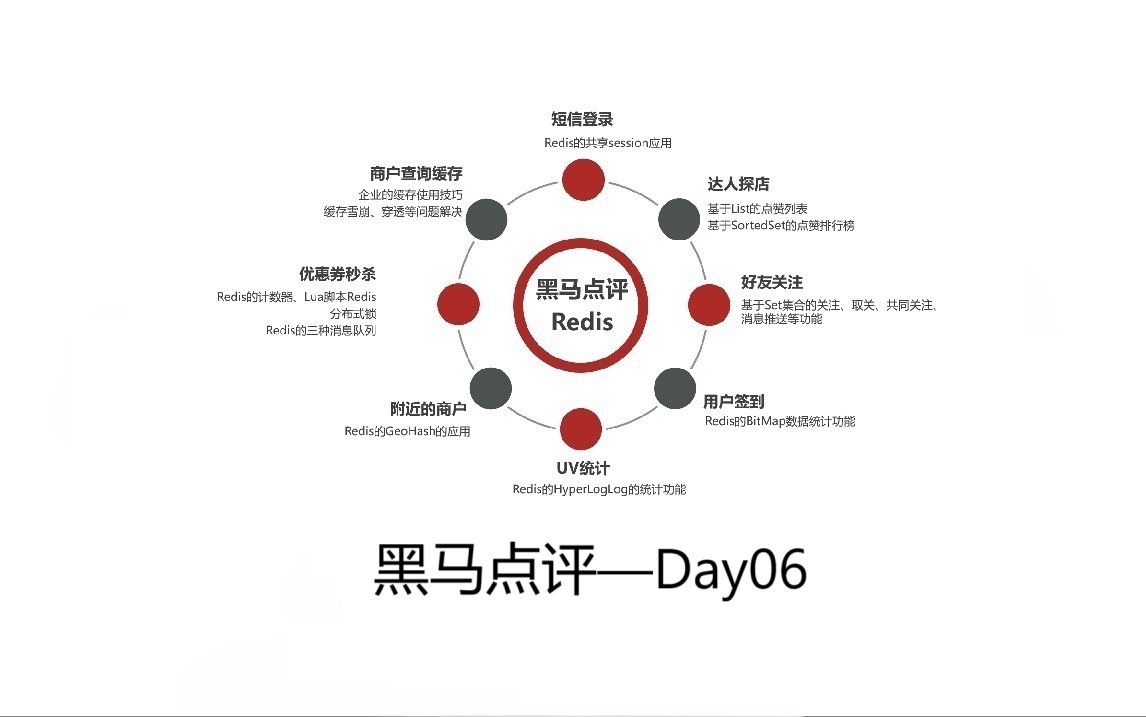
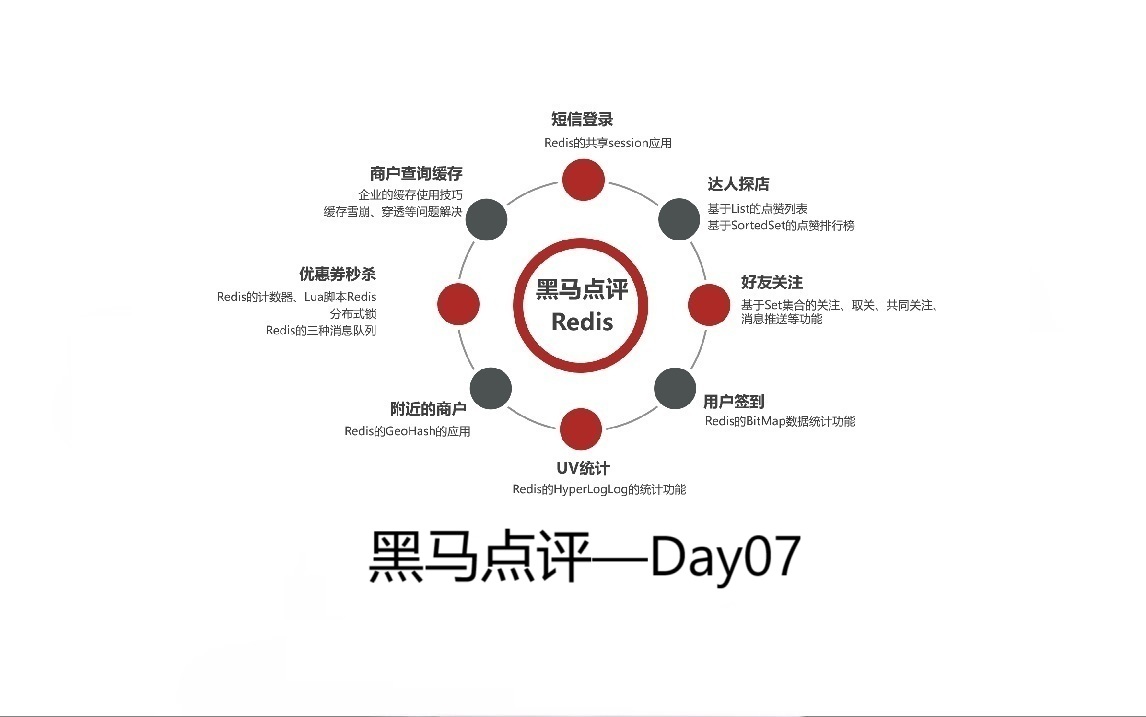
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
| @Slf4j
@Component
public class CacheClient {
private final StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;
public CacheClient(StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate) {
this.stringRedisTemplate = stringRedisTemplate;
}
public void set(String key, Object value, Long time, TimeUnit unit) {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(value), time, unit);
}
public void setWithLogicalExpire(String key, Object value, Long time, TimeUnit unit) {
RedisData redisData = new RedisData();
redisData.setData(value);
redisData.setExpireTime(LocalDateTime.now().plusSeconds(unit.toSeconds(time)));
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, JSONUtil.toJsonStr(redisData));
}
public <R, ID> R queryWithPassThrough(String keyPrefix, ID id, Class<R> type, Function<ID, R> dbFallback, Long time, TimeUnit unit) {
String key = keyPrefix + id;
String json = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (StrUtil.isNotBlank(json)) {
return JSONUtil.toBean(json, type);
}
if (json != null) {
return null;
}
R r = dbFallback.apply(id);
if (r == null) {
stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, "", CACHE_NULL_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
return null;
}
this.set(key, r, time, unit);
return r;
}
private static final ExecutorService CACHE_REBUILD_EXECUTOR = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public <R, ID> R queryWithLogicalExpire(String keyPrefix, ID id, Class<R> type, Function<ID, R> dbFallback, Long time, TimeUnit unit) {
String key = CACHE_SHOP_KEY + id;
String shopJson = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (StrUtil.isBlank(shopJson)) {
return null;
}
RedisData redisData = JSONUtil.toBean(shopJson, RedisData.class);
R r = JSONUtil.toBean((JSONObject) redisData.getData(), type);
LocalDateTime expireTime = redisData.getExpireTime();
if (expireTime.isAfter(LocalDateTime.now())) {
return r;
}
String lockKey = LOCK_SHOP_KEY + id;
boolean isLock = tryLock(lockKey);
if (isLock) {
CACHE_REBUILD_EXECUTOR.submit(() -> {
try {
R r1 = dbFallback.apply(id);
this.setWithLogicalExpire(key, r1, time, unit);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
unlock(lockKey);
}
});
}
return r;
}
private boolean tryLock(String key) {
Boolean flag = stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().setIfAbsent(key, "1", LOCK_SHOP_TTL, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return BooleanUtil.isTrue(flag);
}
private void unlock(String key) {
stringRedisTemplate.delete(key);
}
}
|