2025.04.28
Java 网络编程
一、网络编程概述
1.1 网络编程的概念
- 网络编程:在网络通信协议下,不同计算机上运行的程序,进行的数据传输
- 应用场景
- Java中可以使用java.net包中的类来进行网络编程
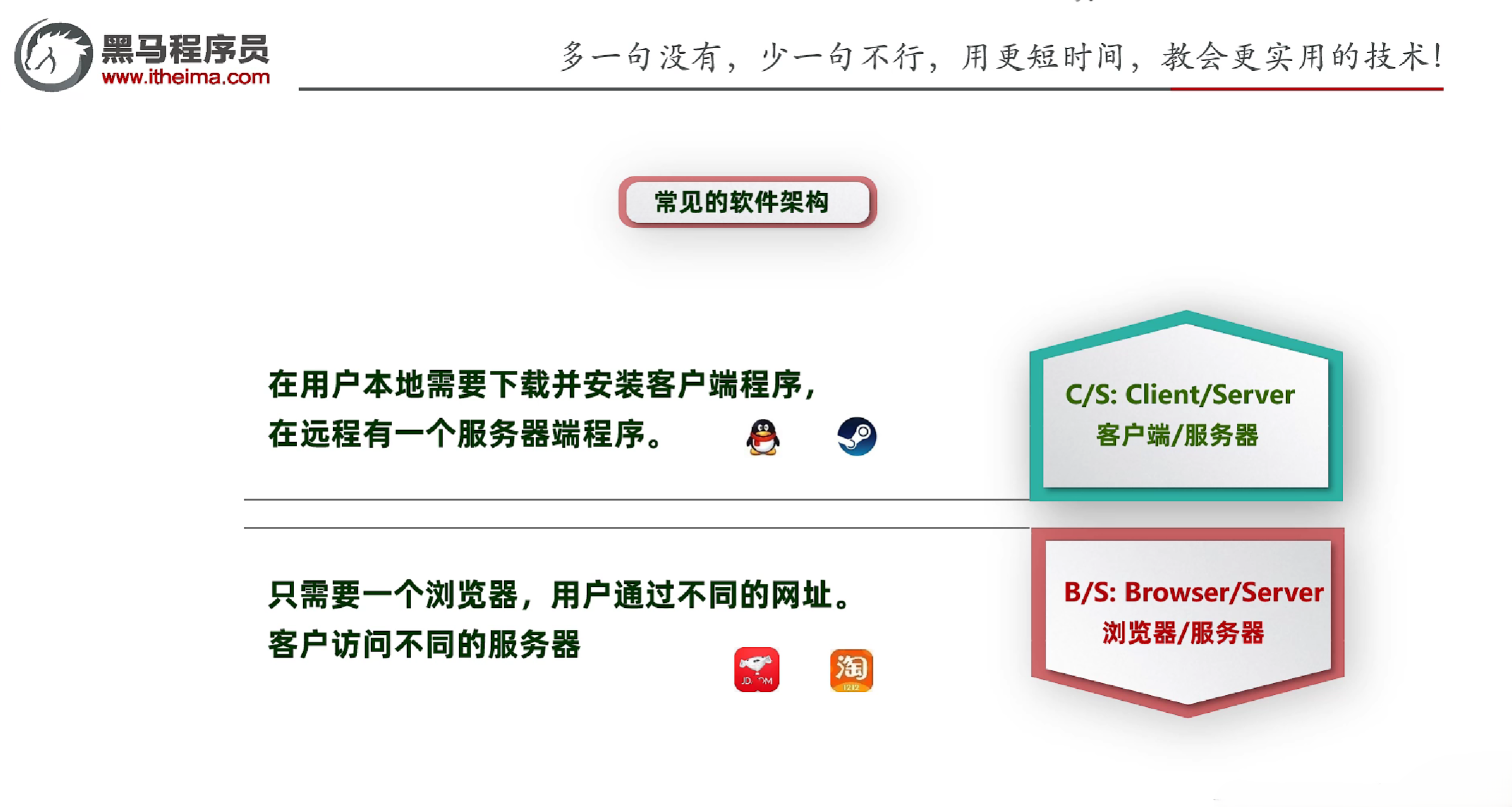
1.2 常见的软件架构
- BS架构:Browser/Server,浏览器/服务器架构
- 典型的BS架构:浏览器+Web服务器+数据库服务器
- 浏览器服务端模式不需要开发客户端
- 优点:跨平台、易于维护、易于升级、易于扩展
- 缺点:性能差、网络延迟大、对网络依赖性强
- 适合移动互联网应用,可以在任何地方随时访问的系统
- CS架构:Client/Server,客户端/服务器架构
- 典型的CS架构:客户端+服务器+数据库服务器
- 客户端服务端模式需要开发客户端
- 优点:性能好、网络延迟小、对网络依赖性小
- 缺点:跨平台差、维护难度大、升级难度大、扩展难度大
- 适合定制专业化的办公类软件,如:IDEA、网游
二、网络编程三要素
2.1 网络编程中的三要素
- IP地址
- 端口号
- 协议
- 数据在网络中传输的规则,常见的协议有UDP、TCP、http、https、ftp等
2.2 IP地址
- IP
- 全称:Internet Protocol,是互联网协议地址,也称IP地址
- 是分配给上网设备的数字标签
- 通俗理解
- 常见的IP分类
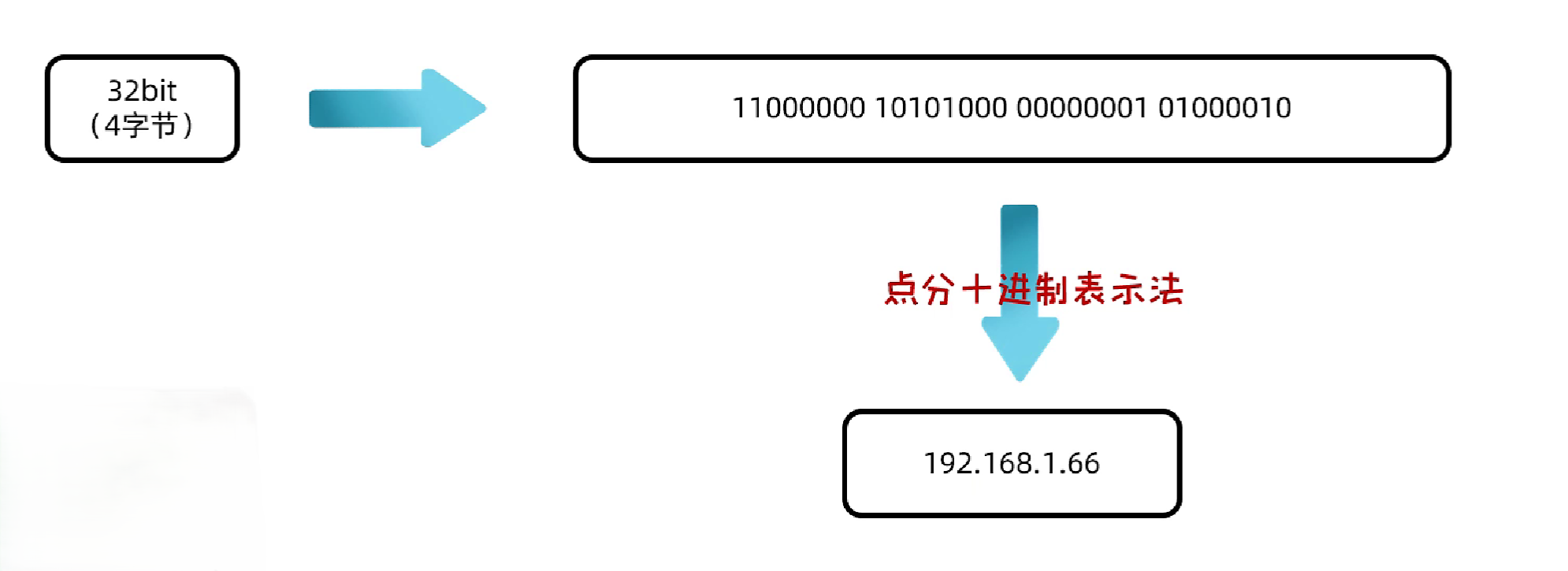
- IPv4:32位二进制数,分为4段,每段8位,范围0-255,通常用点分十进制表示
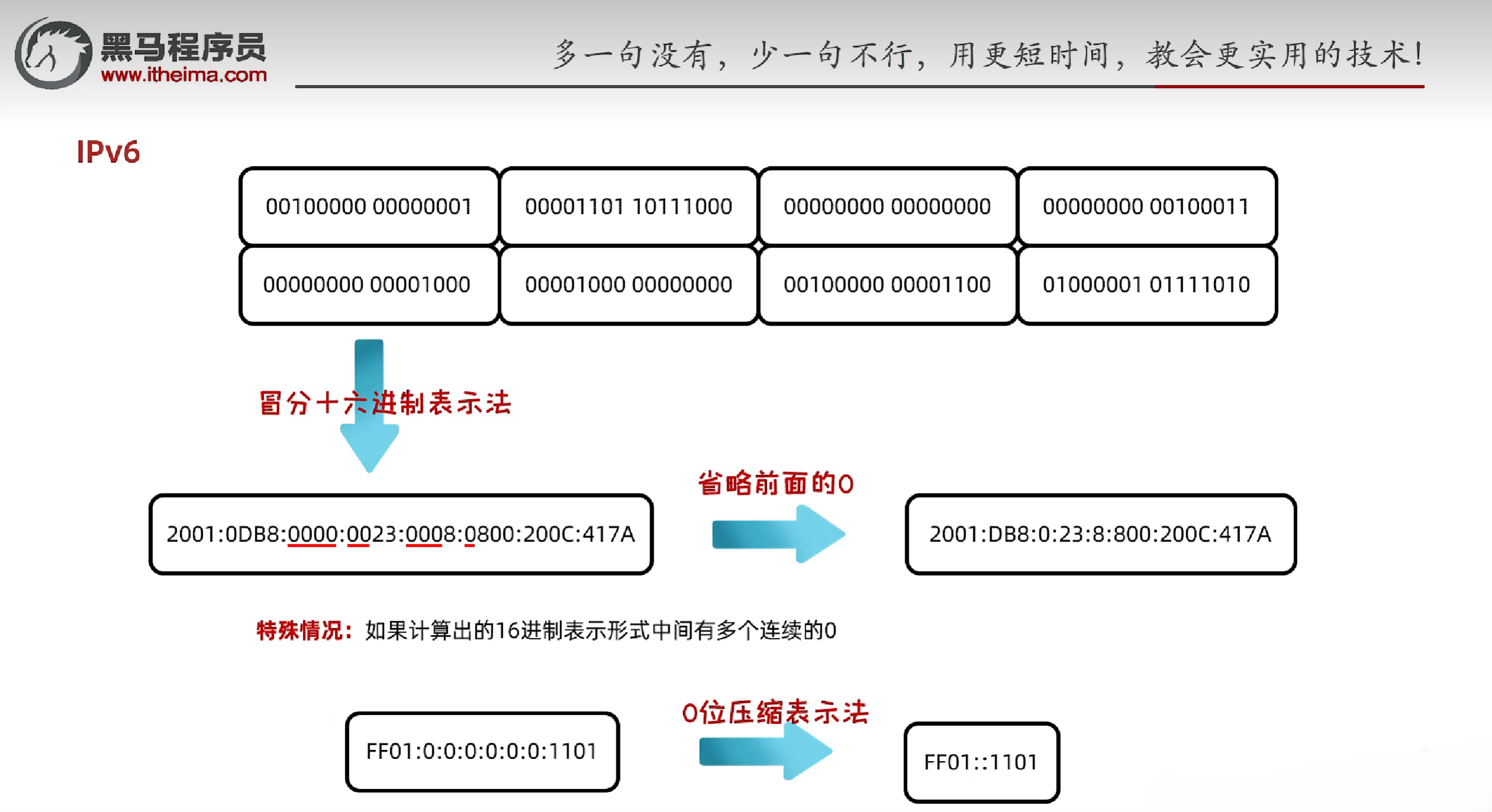
- IPv6:128位二进制数,分为8段,每段16位,范围0-65535,通常用冒分十六进制表示
2.2.1 IPv4
- IPv4
- 全称:Internet Protocol version 4,是互联网通信协议第四版
- 采用32位地址,分为4段,每段8位,范围0-255,通常用点分十进制表示
- IPv4地址分类
- 公网地址(万维网使用)和私有地址(局域网使用)
- 192.168.开头的就是私有地址,范围为192.168.0.0–192.168.255.255,专门为组织机构内部使用,以此节省IP
- 常用的CMD命令
- ipconfig:查看本机IP地址
- ping:测试网络连通性
2.2.2 IPv6
- IPv6
- 全称:Internet Protocol version 6,是互联网通信协议第六版
- 采用128位地址,分为8段,每段16位,范围0-65535,通常用冒分十六进制表示
2.2.3 InetAddress类
- InetAddress类:表示IP地址的类
- 常用方法
- String InetAdress getByName(String host):根据主机名或IP地址获取InetAddress对象
- String getLocalHost():获取本机的InetAddress对象
- String getHostName():获取主机名
- String getHostAddress():获取IP地址
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException {
InetAddress adress = InetAddress.getByName("hansen");
System.out.println(adress);
String hostName = adress.getHostName();
System.out.println(hostName);
String ip = adress.getHostAddress();
System.out.println(ip);
}
}
|
2.3 端口号
- 端口号
- 应用程序在设备中的唯一标识
- 由两个字节表示的整数,取值范围:0-65535
- 其中0-1023是系统保留端口号,不能使用
- 1024-49151是注册端口号,供用户使用
- 一个端口号只能被一个应用程序使用
2.4 协议
- 协议
- 数据在网络中传输的规则
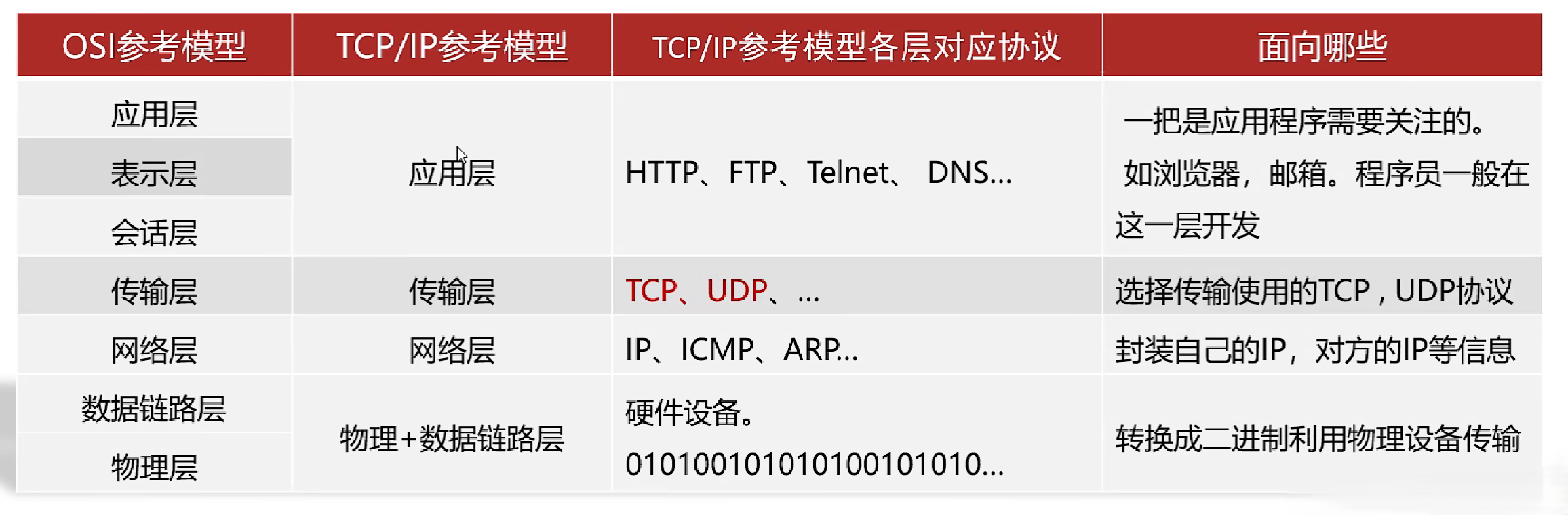
- OSI参考模型:世界互联协议标准,全球通信规范,但模型过于理想化,未能在因特网上进行广泛推广
- TCP/IP协议族:是互联网的核心协议,包含了TCP、UDP、IP等协议
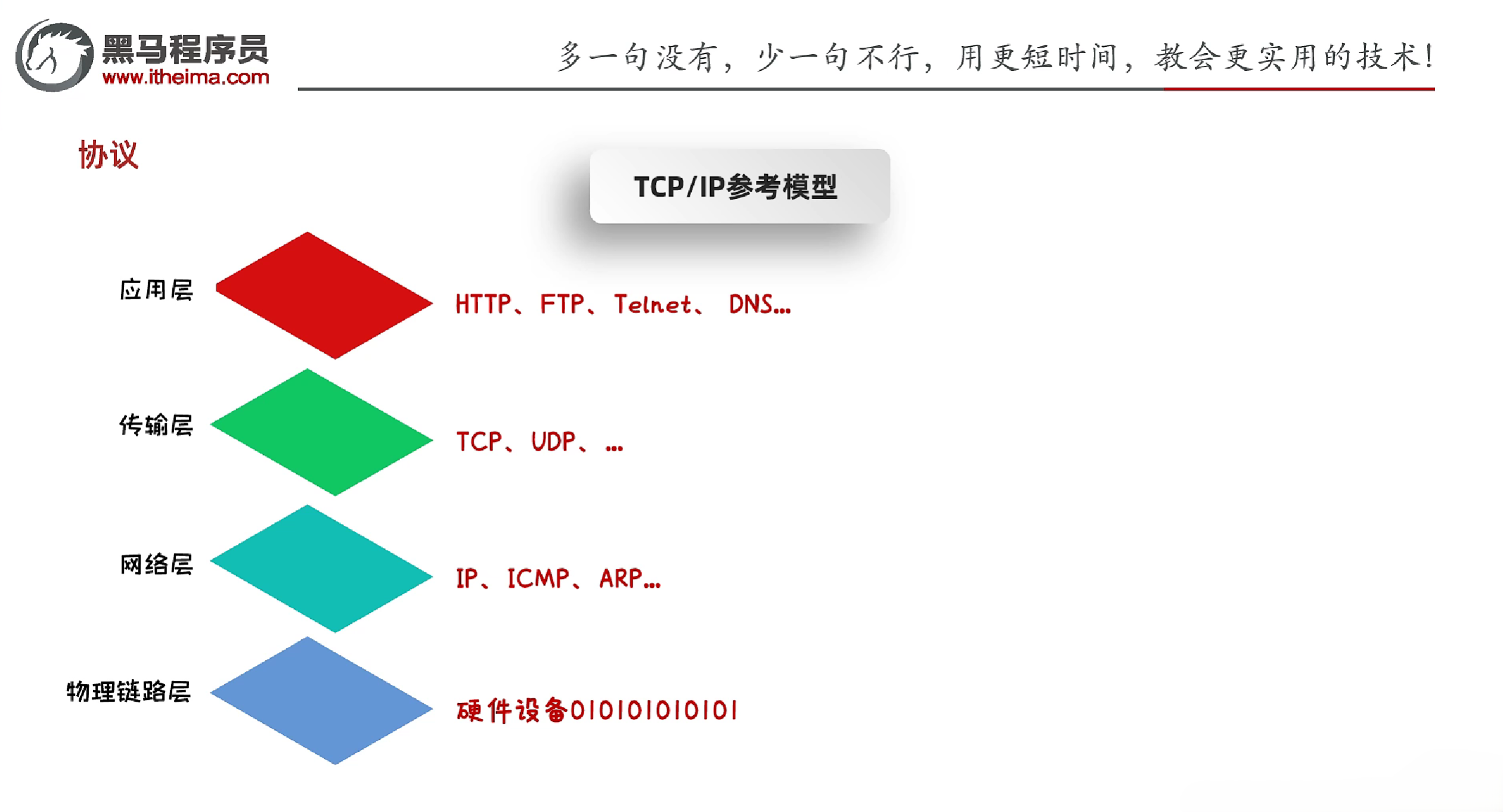
2.4.1 UDP协议
- UDP协议
- 全称:User Datagram Protocol,用户数据报协议
- 无连接的协议,不需要建立连接,直接发送数据
- 不可靠的协议,数据包可能丢失、重复、乱序
- 适合对实时性要求高的应用,如:视频直播、语音通话等
- 传输速度快,开销小
- UDP通信程序(发送数据)
- 创建发送端的DatagramSocket对象
- 数据打包成DatagramPacket对象
- 发送数据
- 释放资源
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
String str = "Hello, World!";
byte[] buf = str.getBytes();
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port = 31412;
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length, address, port);
ds.send(dp);
ds.close();
}
}
|
- UDP通信程序(接收数据)
- 创建接收端的DatagramSocket对象
- 创建DatagramPacket对象,用于接收数据
- 接收数据
- 释放资源
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.SocketException;
public class UDPDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(31412);
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length);
ds.receive(dp);
byte[] data = dp.getData();
int length = dp.getLength();
InetAddress address = dp.getAddress();
int port = dp.getPort();
System.out.println("接收到数据" + new String(data, 0, length));
System.out.println("该数据是从" + address + "这台电脑中的" + port + "这个端口发出的");
ds.close();
}
}
|
2.4.2 UDP协议练习
- 需求:按照下面的要求实现程序
- UDP发送数据:数据来自于键盘录入,知道输入的数据是886,发送数据结束
- UDP接收数据:因为接收端不知道发送端什么时候停止发送,故采用死循环接收
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class UDPSendDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
while (true) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入发送内容:");
String str = sc.nextLine();
if (str.equals("886")) {
break;
}
byte[] buf = str.getBytes();
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port = 1234;
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length, address, port);
ds.send(dp);
}
ds.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.SocketException;
public class UDPReceiveDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(1234);
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length);
while (true) {
ds.receive(dp);
byte[] data = dp.getData();
int length = dp.getLength();
String ip = dp.getAddress().getHostAddress();
String name = dp.getAddress().getHostName();
System.out.println("IP为: " + ip + ",主机名为:" + name + "的人发送了数据:" + new String(data, 0, length));
}
}
}
|
2.4.3 UDP的三种通信方式
- 单播:一对一的通信方式,数据包从一个主机发送到另一个主机
- 组播:一对多的通信方式,数据包从一个主机发送到一组主机
- 组播地址:224.0.0.0~239.255.255.255
- 其中224.0.0.0~224.0.0.255为预留的组播地址
- 广播:一对所有的通信方式,数据包从一个主机发送到网络中的所有主机
组播示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.MulticastSocket;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
MulticastSocket ms = new MulticastSocket();
String str = "Hello World";
byte[] buf = str.getBytes();
InetAddress group = InetAddress.getByName("224.0.0.1");
int port = 224;
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length, group, port);
ms.send(packet);
ms.close();
}
}
|
广播示例:
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
String str = "Hello, World!";
byte[] buf = str.getBytes();
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("255.255.255.255");
int port = 1234;
DatagramPacket dp = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length, address, port);
ds.send(dp);
ds.close();
}
}
|
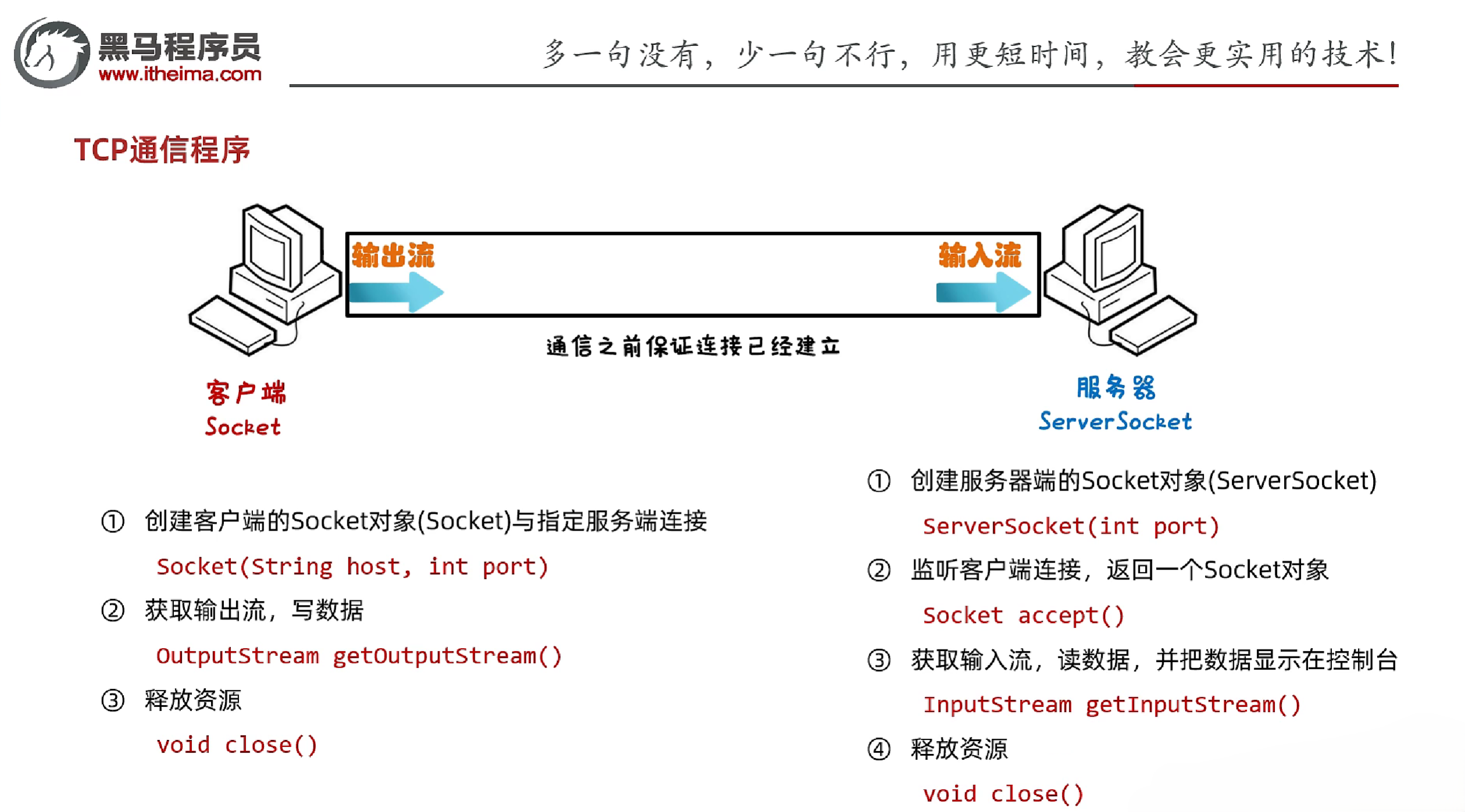
2.4.4 TCP协议
- TCP协议
- 全称:Transmission Control Protocol,传输控制协议
- 面向连接的协议,需要建立连接后才能发送数据
- 通过Scoket产生IO流来进行网络通信
- 可靠的协议,数据包不会丢失、重复、乱序
- 适合对可靠性要求高的应用,如:文件传输、电子邮件等
- 传输速度慢,开销大
- TCP通信程序(发送数据)
- 创建发送端的Socket对象,指定IP地址和端口号
- 获取输出流对象,写数据
- 释放资源
- TCP通信程序(接收数据)
- 创建接收端的ServerSocket对象,指定端口号
- 等待客户端连接,返回Socket对象
- 获取输入流对象,读数据
- 释放资源
示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 10000);
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("Hello World".getBytes());
os.close();
socket.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10000);
Socket socket = ss.accept();
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
int b;
while ((b = is.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) b);
}
socket.close();
ss.close();
}
}
|
2.4.5 TCP传输中的中文乱码问题
- TCP传输中的中文乱码问题:因为TCP传输是以字节为单位的,而中文字符在计算机中是以字节数组的形式存储的,所以在传输过程中可能会出现乱码
- 解决方法:在发送数据时,将字符串转换为字节数组,在接收数据时,将字节数组转换为字符串
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10000);
Socket socket = ss.accept();
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(is);
int b;
while ((b = isr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) b);
}
socket.close();
ss.close();
}
}
|
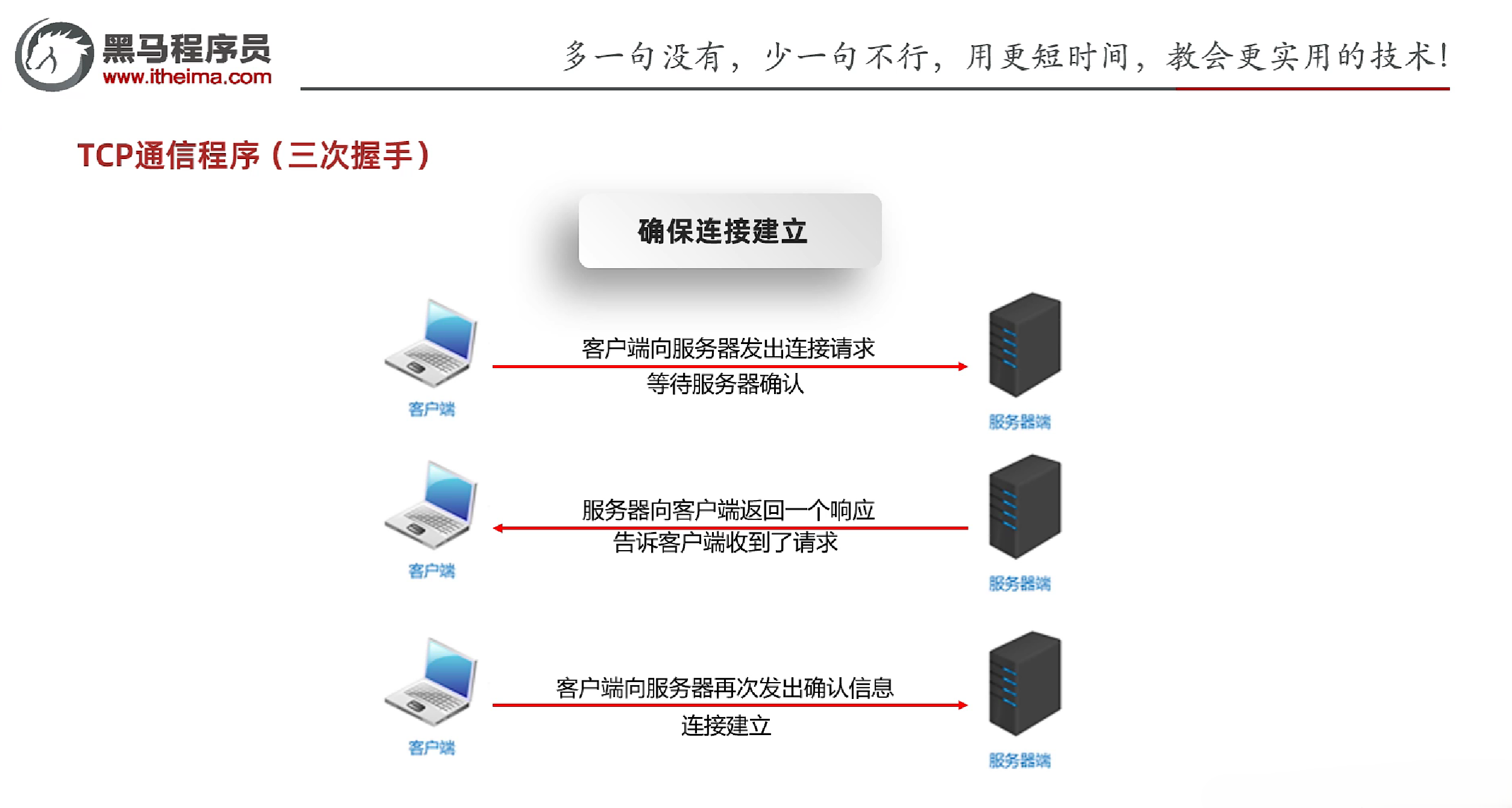
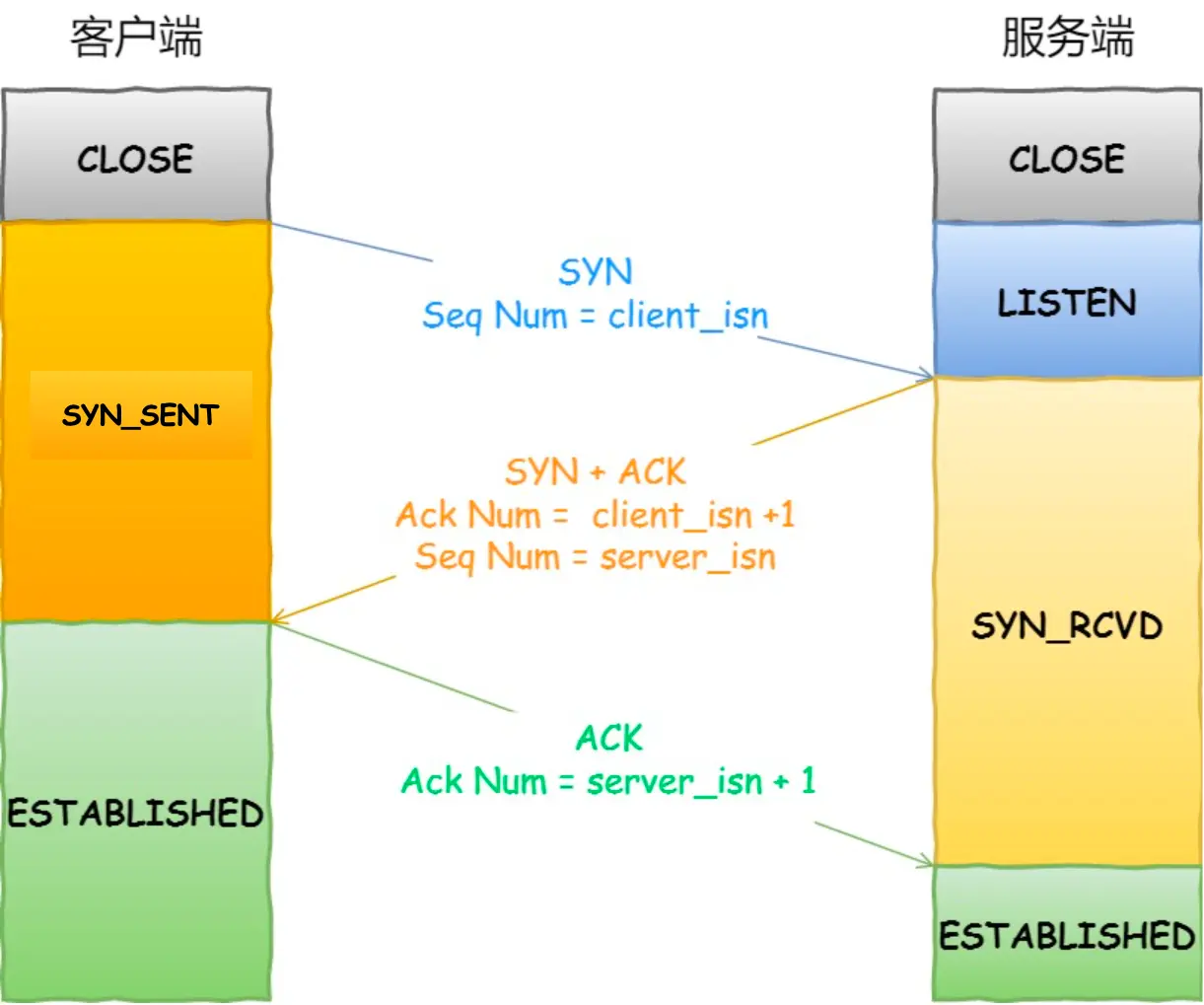
2.4.6 TCP的三次握手和四次挥手
- TCP的三次握手:建立连接的过程
- 第一次握手:客户端发送SYN报文段,进入SYN_SEND状态,等待服务器确认
- 第二次握手:服务器收到SYN报文段,发送SYN+ACK报文段,进入SYN_RECV状态,等待客户端确认
- 第三次握手:客户端收到SYN+ACK报文段,发送ACK报文段,进入ESTABLISHED状态,连接建立成功
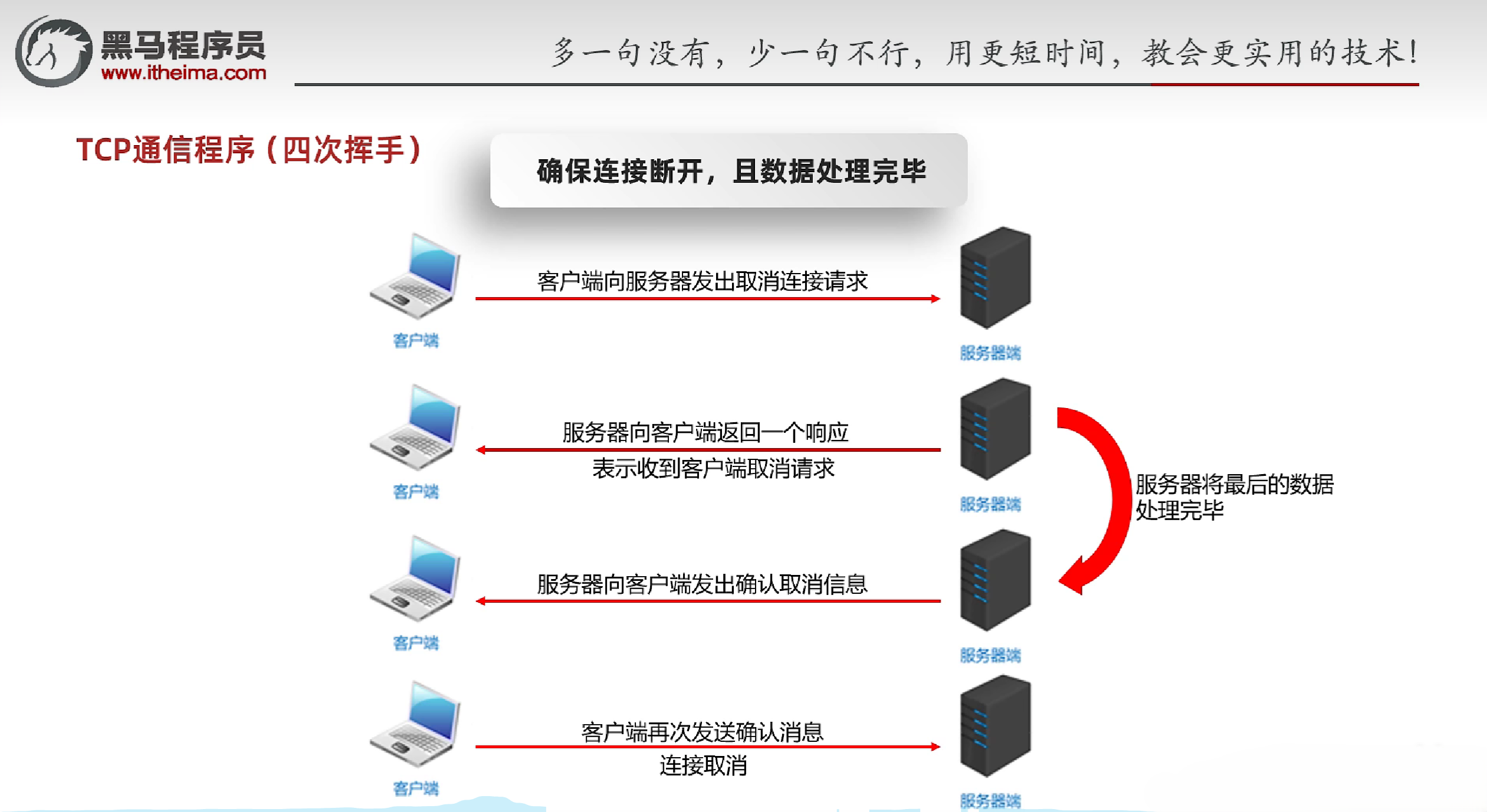
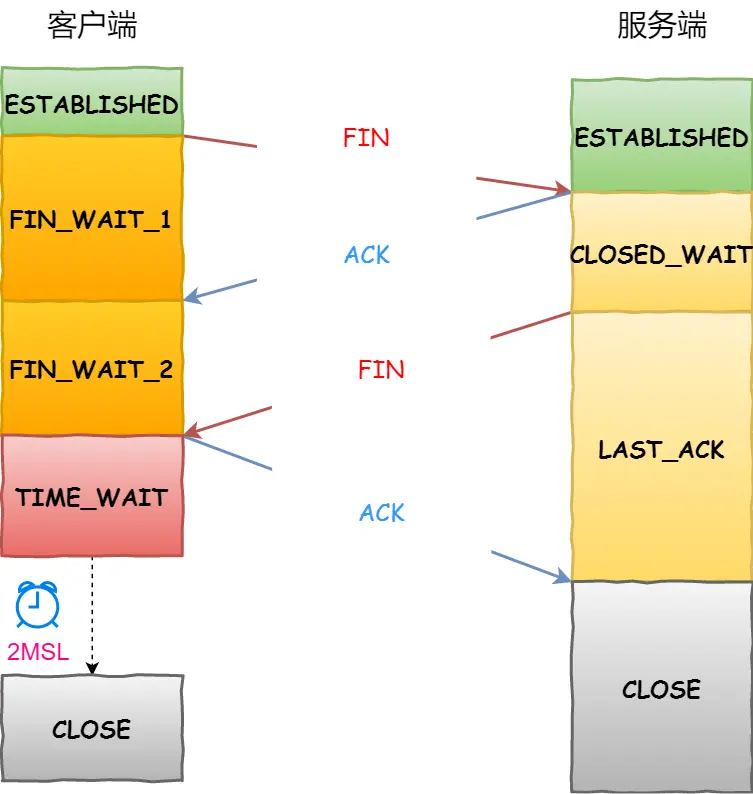
- TCP的四次挥手:断开连接的过程
- 第一次挥手:客户端发送FIN报文段,进入FIN_WAIT_1状态,等待服务器确认
- 第二次挥手:服务器收到FIN报文段,发送ACK报文段,进入CLOSE_WAIT状态,等待客户端确认
- 第三次挥手:服务器发送FIN报文段,进入LAST_ACK状态,等待客户端确认
- 第四次挥手:客户端收到FIN报文段,发送ACK报文段,进入TIME_WAIT状态,等待2MSL后关闭连接
2.5 练习
2.5.1 练习1:上传文件
- 需求:
- 客户端:将本地文件上传到服务器,接收服务器的反馈
- 服务器端:接收客户端上传的文件,上传完毕后给出反馈
- 注意点:
- 在传输文件的循环结束后需要手动flush一下,否则会有最后1kb文件没有传输到服务器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(123);
Socket socket = ss.accept();
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\Java Study\\heima\\NetDemo\\1.png"));
int len;
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
while ((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1){
bos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
bos.flush();
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
bw.write("上传成功");
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
socket.close();
ss.close();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
import java.io.*;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 123);
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\Java Study\\heima\\NetDemo\\gpt.png"));
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(buf)) != -1) {
bos.write(buf, 0, len);
}
bos.flush();
socket.shutdownOutput();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String line = br.readLine();
System.out.println(line);
socket.close();
}
}
|
2.5.2 练习2:解决练习1的重命名问题
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| import java.util.UUID;
public class UUIDDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "");
System.out.println(str);
}
}
|
2.5.3 练习3:上传文件(多线程)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
import java.io.*;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.UUID;
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
public Socket socket;
public MyRunnable(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
public MyRunnable() {
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
String name = UUID.randomUUID().toString().replace("-", "");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\Java Study\\heima\\NetDemo\\" + name + ".png"));
int len;
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
while ((len = bis.read(buf)) != -1) {
bos.write(buf, 0, len);
}
bos.flush();
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
bw.write("上传成功");
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (socket != null) {
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
import java.io.*;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket( 123);
while (true) {
Socket socket = ss.accept();
new Thread(new MyRunnable(socket)).start();
}
}
}
|
2.5.4 练习4:上传文件(线程池)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
import java.io.*;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ThreadPoolExecutor pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
3,
16,
60,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(2),
Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
);
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket( 123);
while (true) {
Socket socket = ss.accept();
pool.submit(new MyRunnable(socket));
}
}
}
|
2.5.5 练习5:BS(接收浏览器消息并打印)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(10000);
Socket socket = ss.accept();
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream());
int b;
while ((b = isr.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char) b);
}
socket.close();
ss.close();
}
}
|
运行Server端后,浏览器输入127.0.0.1:10000,浏览器会发送请求到服务器端,服务器端会打印出请求的内容
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
GET / HTTP/1.1
Host: 127.0.0.1:10000
Connection: keep-alive
sec-ch-ua: "Google Chrome";v="135", "Not-A.Brand";v="8", "Chromium";v="135"
sec-ch-ua-mobile: ?0
sec-ch-ua-platform: "Windows"
Upgrade-Insecure-Requests: 1
User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/135.0.0.0 Safari/537.36
Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*
|
参考资料:
[1] 黑马程序员Java零基础视频教程_下部
[2] 小林coding